Managing cash is vital for running a successful business. That is why reviewing your company’s cash flow statement regularly is so important.
CASH IS KING
Your cash flow statement provides important context to information that might not appear on a different financial statement. For example, revenue from a new sale often appears on an income statement and contributes to the company’s overall profit or loss. However, if an invoice isn’t due immediately or the company extends a line of credit to the customer, the actual cash may not hit the company’s bank account for months.
BREAKING IT DOWN
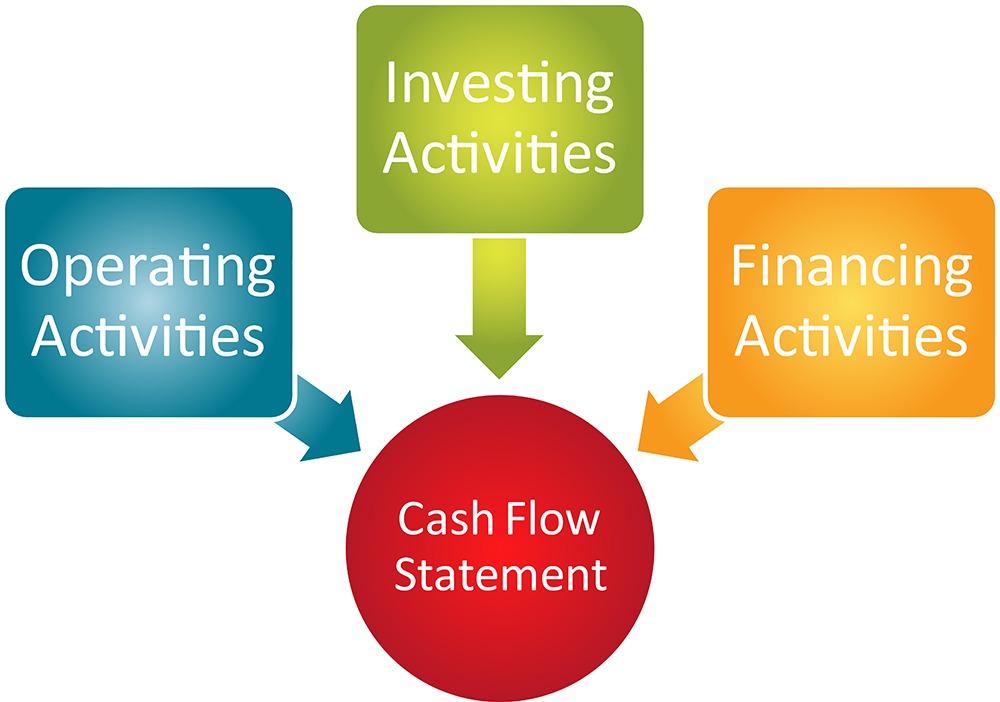
A cash flow statement is broken into three sections to show the primary sources and uses of your cash.
- Cash flow from operations presents the cash inflow and outflow from your company’s revenue-generating activities. It starts with net income and adds or subtracts the types of cash activities many people automatically associate with running a business: revenue from customers, wages to staff, inventory purchases, and income taxes.
- Cash flow from investing activities includes sources and uses of cash for things like the purchase or sale of physical assets, investment in securities, or the sale of securities.
- The financing section outlines how cash is used in any type of financing activities, including debt, equity, or dividends.
WHAT TO WATCH FOR
Though a cash flow statement can’t tell you everything about a company’s financial viability, there are some things to watch out for that can be particularly revealing.
Is there a positive cash flow coming from your core business operations?
Also, look at the financing section. Are you bringing in most or all your cash from loans? This might be okay for a startup business, but not for a company that’s established.








