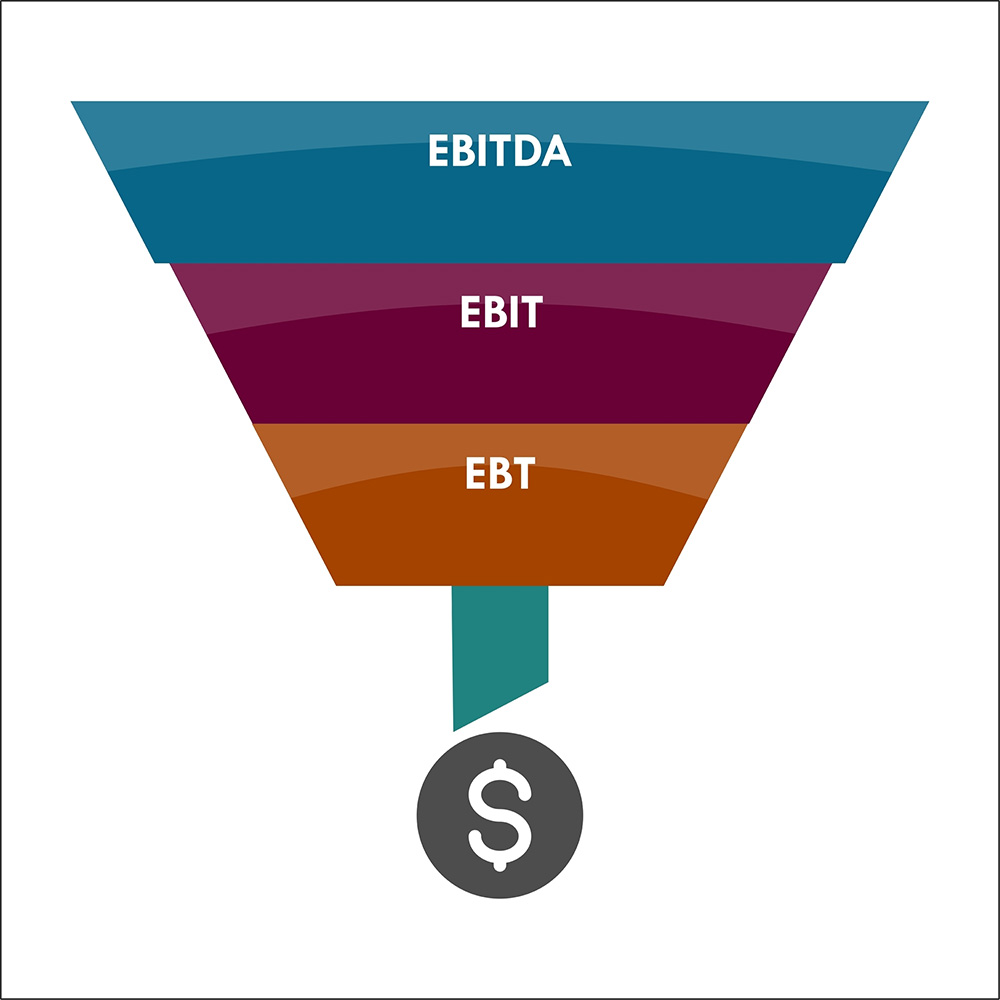
EBITDA, or Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization, is a financial metric used to evaluate a company’s operating performance. It measures profitability from its core business activities by excluding non-operating expenses, such as interest and taxes, as well as non-cash charges, including depreciation and amortization. This provides a clearer view of a company’s cash flow and operational efficiency, making it easier to compare firms across industries.
To calculate EBITDA, start with net income, then add back interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization expenses from the income statement. It’s widely used by investors and analysts to assess a company’s financial health, especially for businesses with high debt or significant assets.
However, EBITDA has limitations. It doesn’t account for capital expenditures or changes in working capital, which can impact actual cash flow.
Understanding EBITDA is essential for spring financial reviews to gauge business performance and plan strategically.

